How to measure leaf springs?

A leaf spring is a critical component of the suspension system used in cars, trucks, trailers, and agricultural machinery. It carries vehicle load, maintains ride height, and contributes to driving stability and comfort. Accurate measurement of a leaf spring is essential when replacing a worn or broken unit, selecting an equivalent alternative, or manufacturing a custom spring. Incorrect measurements may result in improper installation, uneven load distribution, accelerated tire wear, or suspension failure.
This article provides a professional, step-by-step approach to measuring a leaf spring based on industry and workshop best practices.
When Leaf Spring Measurement Is Required
Leaf spring measurement is necessary in the following situations:
- replacement of damaged or fatigued springs;
- selection of an aftermarket or non-original equivalent;
- custom manufacturing of a leaf spring;
- suspension modification to increase or reduce load capacity;
- technical inspection and suspension diagnostics.
Required Tools
For accurate and repeatable measurements, the following tools are recommended:
- tape measure or steel ruler (minimum length 1.5–2 m);
- vernier caliper or micrometer for thickness measurements;
- flat reference surface or measuring table;
- marker or chalk for reference marks;
- jack and safety stands if the spring is measured on the vehicle.
Key Leaf Spring Parameters
To correctly identify or reproduce a leaf spring, all major geometric and structural parameters must be recorded.
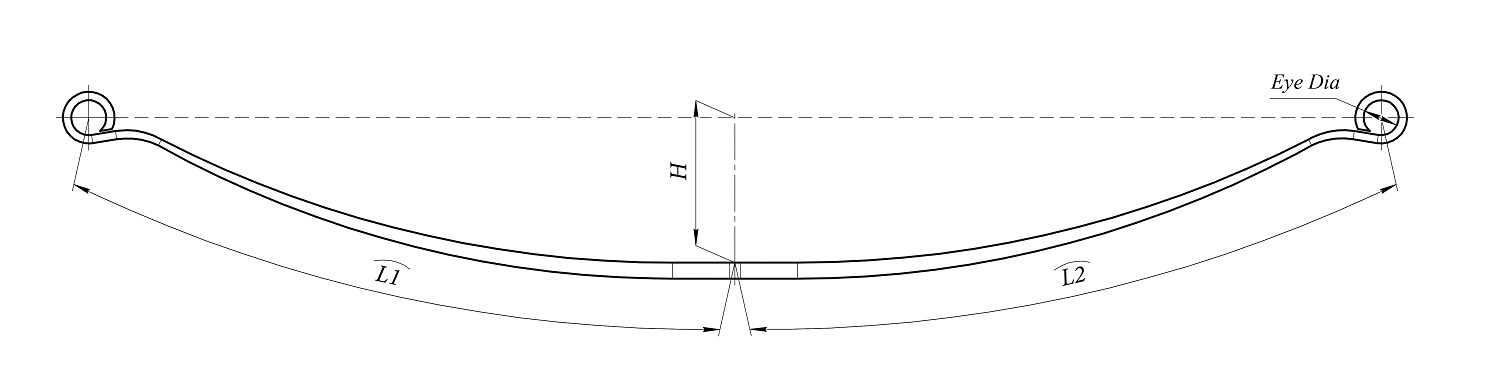
1. Overall Length
The overall length is measured from the center of the front eye to the center of the rear eye.
For asymmetric leaf springs, two additional dimensions are critical:
- distance from the front eye center to the center bolt (L1);
- distance from the center bolt to the rear eye center (L2).
These measurements ensure correct axle positioning during installation.
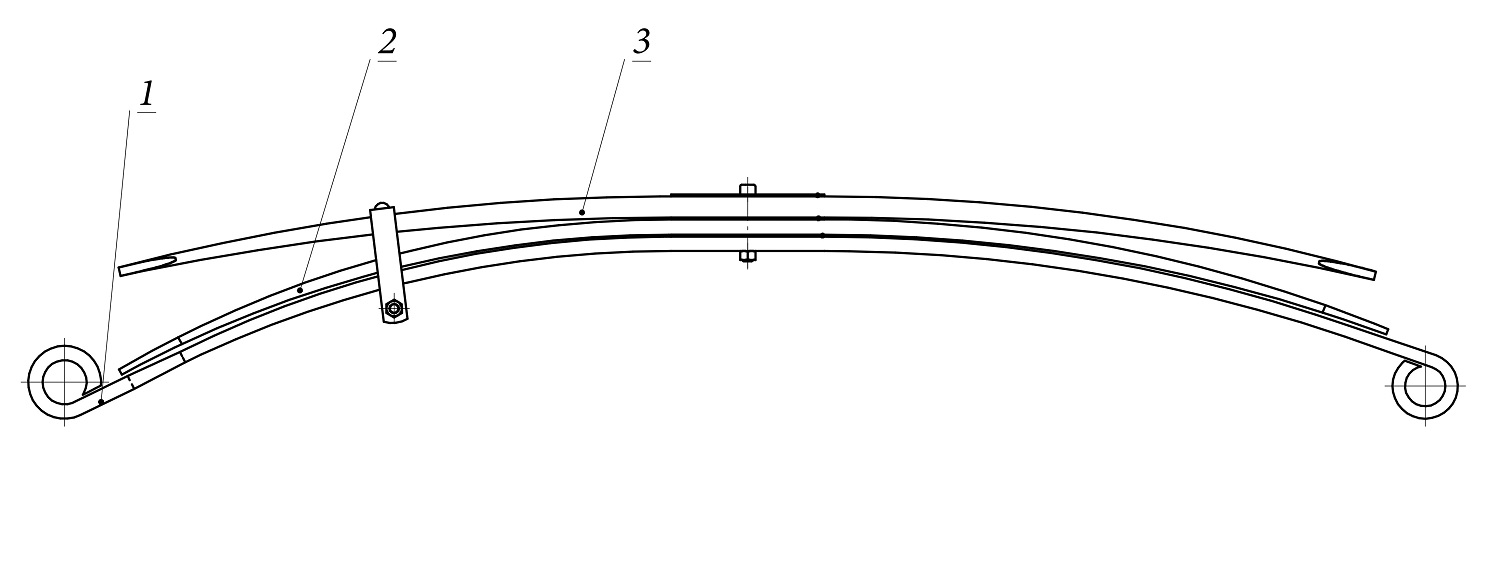
2. Number of Leaves
Count the total number of leaves in the spring pack, including the main (master) leaf. Auxiliary or overload leaves must also be included, as they affect load capacity and spring rate.
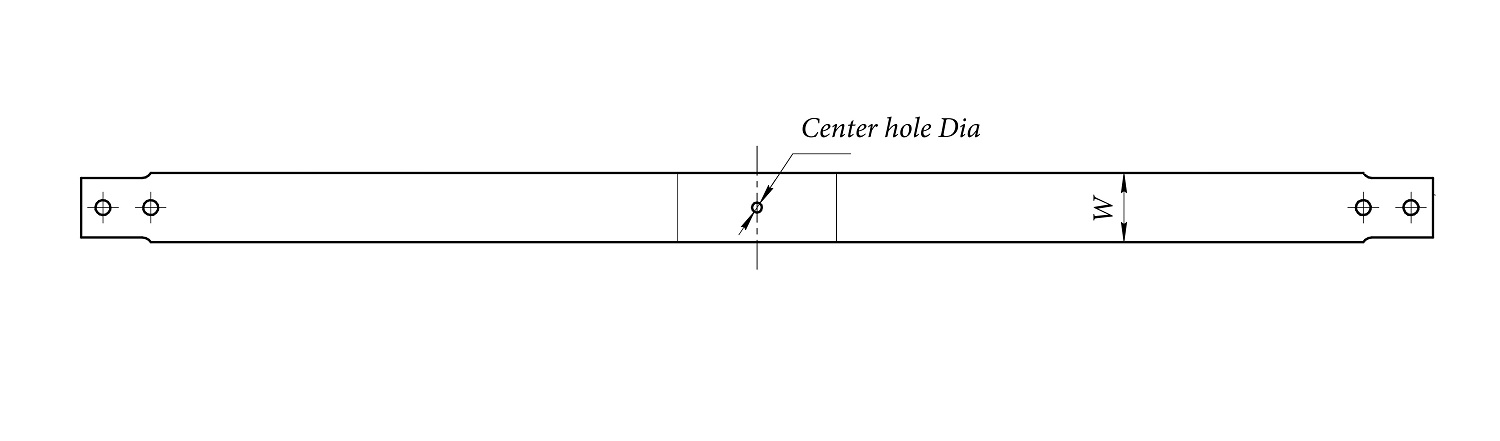
3. Leaf Width
Measure the width of the leaves (W) in the central section using a caliper. Common standard widths include 40, 50, 60, 70, and 90 mm, depending on vehicle class.
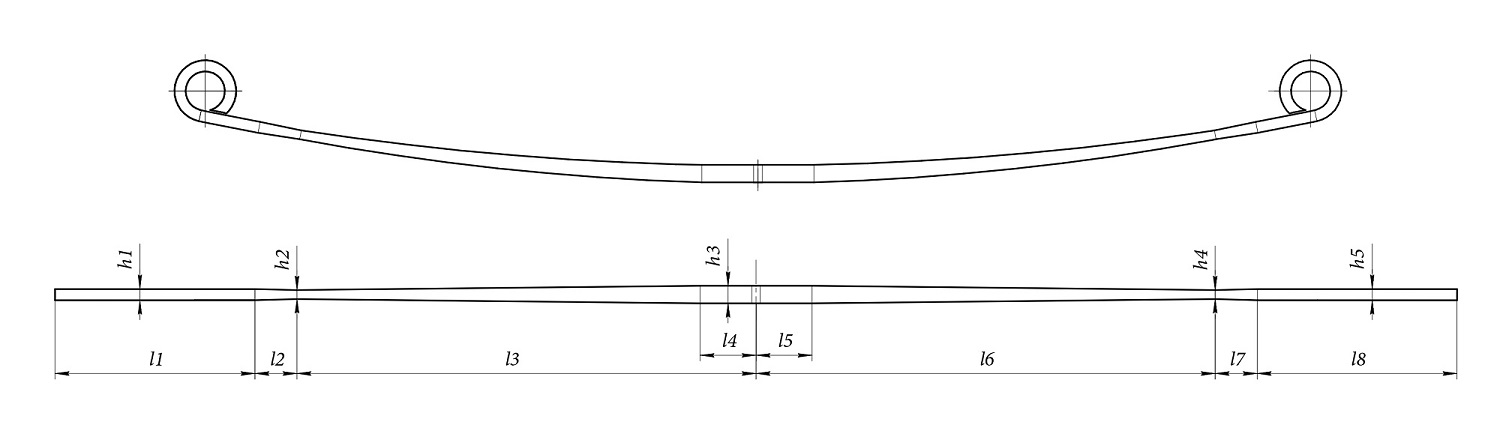
4. Leaf Thickness
Each leaf should be measured individually. In professional applications, it is important to verify whether all leaves have uniform thickness (h) or if a progressive design is used. For parabolic leaf springs, measure the plate (the thickest part) and measure the thickness at 100 mm intervals.
5. Arch Height (Camber)
The arch height (H), also known as camber, is the vertical distance between the imaginary straight line connecting both eye centers and the highest point of the spring, typically near the center bolt.
Measurement procedure:
- Place the leaf spring on a flat surface with the eyes facing downward.
- Establish a straight reference line between the eye centers.
- Measure the vertical distance to the highest point of the spring.
Camber directly influences ride height, suspension stiffness, and load behavior.
6. Spring Eyes and Bushings
Record the following parameters:
- inner diameter of the bushing;
- outer diameter of the spring eye;
- bushing type (rubber, polyurethane, bronze);
- presence of a steel sleeve or lubrication channel.
These details are essential for proper mounting and durability.
7. Center Bolt and Retainers
Measure and note:
- center bolt diameter;
- bolt length and head height;
- number and position of rebound clips or retainers that secure the leaf pack.
Measuring a Leaf Spring Installed on the Vehicle
If removal is not possible, measurements can be taken with the spring installed, but certain limitations apply:
- the vehicle must be positioned on a level surface;
- the suspension should be unloaded;
- camber measurements must account for vehicle weight and static load.
For maximum accuracy, removing the leaf spring is strongly recommended.
Common Measurement Errors
Typical mistakes include:
- ignoring spring asymmetry;
- measuring worn or deformed bushings without correction;
- confusing overall length with mounting length;
- inaccurate camber measurement due to uneven reference surfaces.
Accurate leaf spring measurement is a systematic process that requires precision and attention to detail. Recording all geometric and structural characteristics ensures correct replacement, safe operation, and long service life of the suspension system. In professional environments, comprehensive measurement is the foundation of reliable suspension performance.